Do you remember Cher singing “If I could turn back time” aboard U.S.S Missouri back in 1989? Well, that’s exactly what ECB did with EGB yields and PEPP expectations: the time is turned back and yields are where they were before the pandemic (if not even lower). But are there any laggards, any late bloomers in the fixed income spave that might follow up in weeks ahead? Find out in this brief research piece.
European Central Banks’ Governing Council meets every six weeks and the next GC meeting is scheduled for December 10th, 2020 – so put this date on your calendar if you already haven’t. Meanwhile, we can easily conclude that the pressure on ECB’s GC was extraordinarily high yesterday. For instance, the first question in Q&A session following the introductory statement was “how much you might enlarge your support programme by December, and which instruments you primarily have in mind?”. ECB’s Chairwoman Christine Lagarde highlighted once again that risks are “clearly, clearly” tilted to the downside, that the Frankfurt-based monetary institution would look at all the instruments at its’ disposal and the central bank has already acted promptly and appropriately in the past. We could conclude that Frankfurt reasoned it’s too early to act in October since “soft lockdowns” in Germany and France haven’t yet started. Instead, the message ECB delivered yesterday could be summed up in three simple statements:
things are bad and we acknowledge it,
we will act appropriately, as we did in the past,
our action will follow on December 10th meeting.
Reading between the lines, one can extract some additional guidelines from Lagarde’s statement. ECB acknowledged that in the third quarter credit conditions regarding loans to firms tightened. Bank lending survey indicated that net demand for loans from corporates weakened (this is probably because corporate investment ebbed), while net demand from households strengthened. Since banks’ balance sheets remain supportive, it’s obvious that it’s their attitude towards risk that might be the issue causing slower loan generation. This means that ECB might strengthen TLTRO-III instrument in December, allowing banks to get cheap funding that can be transferred to corporates.
Lagarde also commented on EA inflation figures turning red all over again (EA CPI YoY @ -0.3%), stating that there were multiple forces in September pushing down overall price levels: German VAT reduction, seasonal summer sales and continuation of garment sales etc. Surprisingly, ECB called this “negative inflation”, distinguishing it from deflation by not being persistent and not feeding upon itself (meaning that it might disappear over time). Even with negative inflation being seen as transitory, ECB Chairwoman highlighted the benefits of PEPP – namely it’s flexibility. This emphasis strengthened the confidence of bond investors that the emergency facility might be extended up until the end of 2021 and expanded by additional 400bn EUR to 1.75bn EUR total. Let’s do a quick figure check: PEPP was announced in March and initially set to 750bn EUR; then in June it was increased by 600bn EUR to the current value of 1.35tn EUR; with a possible December expansion it would reach staggering 1.75tn EUR. It’s worth remembering that in 2Q2020 EA total government debt stood at 10.9tn EUR (95% EA GDP), while security-related debt reached 8.9tn EUR (81.6% GDP), meaning that with December expansion PEPP purchases would relieve about 20% of total EA sovereign debt paper. It’s also worth remembering that EA security-related debt increased by 755bn EUR in 2Q2020 compared to the same time last year and with fiscal deficit already financed by now (some countries like Slovenia even did 2021 pre-financing), the sheer size of second PEPP expansion might spell EGB bond scarcity (in case you haven’t thought of that before).
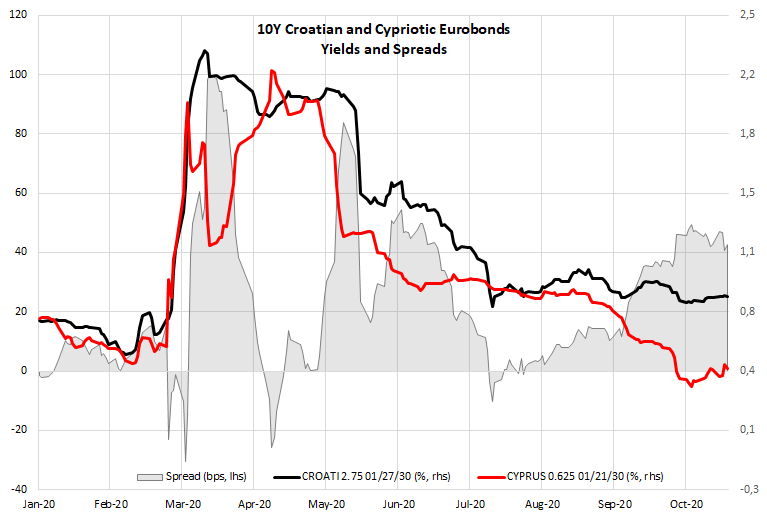
How is all this affecting CROATIs? First of all, let’s take a look at CROATI-CYPRUS 10Y YTM spread depicted above. We’re comparing Croatia to Cyprus since countries have similar levels of public debt (CRO 85.3% GDP, CYP 113.2% GDP, the difference is much lower if we allow ourself the mental flexibility to exclude the 4.1bn EUR of Cypriotic bonds already on ECB’s balance sheet; without this partition, Cypriotic debt would be around 94% GDP) and equal credit ratings (BBB-, stable outlooks according to Fitch and S&P). Higher public debt in the case of Cyprus could be offset by insular country’s EA membership. As a matter of fact, the two bonds were traded at roughly equal yield in mid-summer. In period August-October the two papers diverged with CROATIs threading water, while Cypriotic yield contracted from 0.875% (beginning August) to the current value of 0.415%. We think this was not due to the existing PEPP package since ECB bought 481mm EUR of Cypriotic bonds in March-May, 455mm in June-July and merely 257mm EUR in August-September (pushing the total PEPP sum up to 1.2bn EUR; security-related debt of Cyprus is 16.3bn EUR). You see our point: in months when most of the yield contraction happened, ECB was actually buying only half of what it bought in peak months; so the contraction couldn’t stem from this force alone. Instead, we think that with Covid cases surging across Europe, the market already started to price in an extension of PEPP. Recent “soft lockdowns” in Germany and France merely cemented ECB’s resolve. We stick to the opinion that augmented PEPP was gradually calculated in periphery yields and is by now mostly priced in, but has yet to be calculated into CROATIs through tighter spreads.
The main question we need to answer right now is – what are the chances of Croatian bonds following the trajectory of EGBs? We consider this to be very likely as we have seen ECB spillovers into CROATIs in the past. As a matter of fact, this might be the reason why recent sell off on long CROATIs was much shallower compared to ROMANIs, for instance. For instance, last week CROATI 1.5 06/17/2031 (the new and most liquid paper on CROATI curve) was traded at 105.70 and with this week’s sell off bids barely managed to drop below 104.90. As a matter of fact, yesterday we saw larger bids on this one (10mm+), first at 104.90, and then gradually moving up to 105.20. If you type MOSB on Bloomberg and filter only this paper, you can see that yesterday not a single trade got executed below 105.00 level. Actually, we can do this for you:
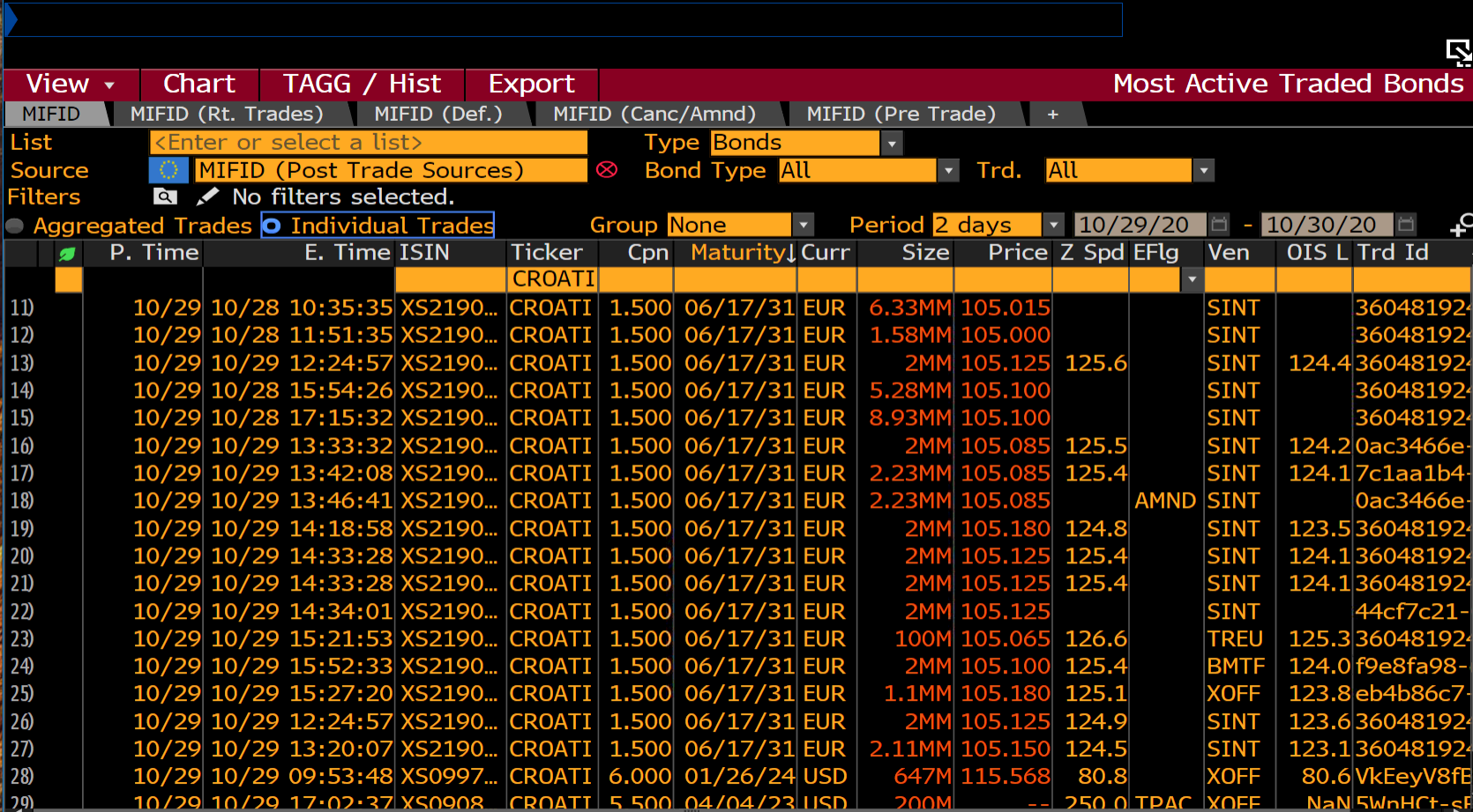
CROATIs are cheap in relation to similar EGBs, you can name your benchmark (BTPs, PGBs, CYPRUS, SPGBs etc.). This might be the reason why sell offs could be shallow in the future as well. Also sine January this year average spread of CROATI 2.7 01/27/2030 to CYPRUS 0.625 01/21/30 was 23bps. This means that if Croatia reverts to mean and Cyprus stays where it is, CROATI 2.7 01/27/2030 should be traded at 0.65% (0.42% + 0.23% = 0.65%). Since CROATI 1.5 06/17/2031 (a more liquid paper) usually trades at 10bps-15bps above CROATI 2.7 01/27/2030 (CRO30 have a shorter maturity and are much scarcer), this would give it a fair valuation of 0.74%-0.79% in terms of YTM (clean price range between 107.20-107.70). From this point of view, if Croatian bonds mean revert in the process of pricing in new ECB stimulus, this could equal some two big figures worth of capital gains (the paper is currently offered at 105.40). Not bad for an early Christmas gift.
TNG published their 9M 2020 results, showing a 7.7% YoY decrease in sales, meanwhile EBITDA was up 8% YoY and net profit rose 75.5% YoY to HRK 30.8m.
In 9M period TNG posted sales in the amount of 185.7m, representing a decrease of 7.7% YoY. The decrease comes as a result of docking three tankers and less presence of TNG’s fleet at the spot market where the ship owner generates nominally higher income but is also burdened by higher costs due to the nature of the business in which the ship owner covers voyage related costs.
TNG’s 9M Financials
The average daily TCE of the fleet during the first half of 2020 was recorded at USD 15,221, representing a 5% YoY increase. Meanwhile fleet utilization amounted to 94.3%. Lower utilization comes as a result of the aforementioned docking.
TNG’s historic TCE
Commissions and voyage associated costs amounted to HRK 25.3m in the first nine months of 2020, while in the same period of 2019 they added up to HRK 44.9m. The decrease in these expenses is due to less exposure of TNG’s fleet in the spot market. Operating expenditures of the fleet amounted to HRK 73.2m in the first nine months of 2020 and have slightly increased from the same period of 2019 when they were HRK 70.5m, while general and administrative expenses recorded at HRK 4.8m are slightly up against the same period last year.
As a result, EBITDA rose 8% YoY, amounting to 85.9m.
Below the operating line, TNG’s net financial loss amounted to HRK -15.6m, representing a 31.6% YoY improvement. Finally, net profit amounted to HRK 30.8m, representing an increase of 75.5% YoY.
Turning our attention to the balance sheet, TNG was able to decrease their net debt by 6.7% since the beginning of the year with net debt amounting to HRK 458.9m. This translates to 3.9x net debt/EBITDA. According to the Management, the decrease in debt is in accordance with the loan repayment plans of TNG and regular decrease in indebtedness, while a further decrease in the company’s debt is expected in the future.
The management provided a calculation of NAV per share, putting it at USD 8.99 (cca HRK 58.3). This would indicate that TNG is currently traded 22.8% below the NAV of their vessels. However, they highlighted that the assessment was based on current market conditions (revenue and cost assumptions of typical average product tanker) which show strong fluctuations and do not take into account TNG specifics and management expectations.
TNG’s Historic NAV per share
IMO 2020
Note that in Q3 TNG installed the required ballast water treatment system in 2 of 3 tankers that had their regular five-year dry dock.
Based on the dockings done so far, the Management concludes that the actual costs are in line with the plan. In other words, the average cost of delivery and installation of BWTS and the cost of docking amounted about 1.5m USD per ship, keeping in mind that the ECO tanker Dalmacija was delivered from the shipyard as a new building with an already implemented ballast water treatment system
In 9M of 2020, the company recorded an increase in sales of 8.7%, an increase in EBITDA of 32.4% and an increase in net profit of 37.1%
As Končar D&ST, a part of the Končar Group, published their 9M 2020 report, we are bringing you key takes from it. According to the report, in the first nine months of 2020 the company recorded sales of HRK 813.1m, representing an increase of 8.7%. We note that the company did not provide almost any comments on their 9M performance, however one should note that the company increased its stake in Power Engineering Transformatory (PET) by 26% in Q2. This way Končar D&ST increased its stake in PET to 100%. As a reminder, PET is a Polish manufacturer of power transformers from 6,3 to 63 MVA and up to 145 kV .
The Management Board stated that they assess that the general condition of the Group as stable, while they are continuously carrying out activities of streamlining of business, cost reduction, contracting new business in general to raise the competitive advantages of the Končar D&ST on the market.
Turning our attention to operating expenses, they amounted to HRK 827.35m, which is an increase of 8.7%. Such an increase could mostly be attributed to higher material costs by 12.5% or HRK 77.9m, which was partially offset by changes in the value of inventories of work in progress and finished goods which amounted to HRK -42.3m.
As revenue growth outpaced the growth of operating expenses, EBITDA is up by as much as 32.4% to HRK 62.58m. Such a result notes an improvement of the EBITDA margin by 1.3 p.p. YoY to 7.3%. Meanwhile, operating profit is up by 30.9% (or HRK 10m) and stands at HRK 42.4m.
Going further down the P&L, the company witnessed somewhat lower net financial loss of HRK -49k, compared to HRK -115k in 9M 2019.
In 9M of 2020 Končar D&ST noted a net profit of 34.57m, representing an increase of 37.1%. Such a result puts the profit margin at 4% (+0.8% p.p. YoY).
Looking at CAPEX, in 9M the company invested HRK 34.53m compared to HRK 70.4m in the same period of the previous year. The company added that the finalization of the planned investment in increasing the production capacity of distribution transformers is in place, while its completion is expected in Q4 of this year.
